- About CDC
- Diseases & Conditions
- Programs & Campaigns
-
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
- National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
- Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal
- International Cooperation
-
About CDC
- Diseases & Conditions
-
Programs & Campaigns
-
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
-
National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
-
Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Weekly Report 2025
- Weekly Report 2024
- Weekly Report 2023
- Weekly Report 2022
- Weekly Report 2021
- Weekly Report 2020
- Weekly Report 2019
- Weekly Report 2018
- Weekly Report 2017
- Weekly Report 2016
- Weekly Report 2015
- Weekly Report 2014
- Weekly Report 2013
- Weekly Report 2012
- Weekly Report 2011
- Weekly Report 2010
- Weekly Report 2009
- Weekly Report 2008
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal
- International Cooperation
- News
- Privacy Policy
- Security Policy
- Government Website Open Information Announcement
- Copyright Notice on Health Educational Materials
Background
Varicella
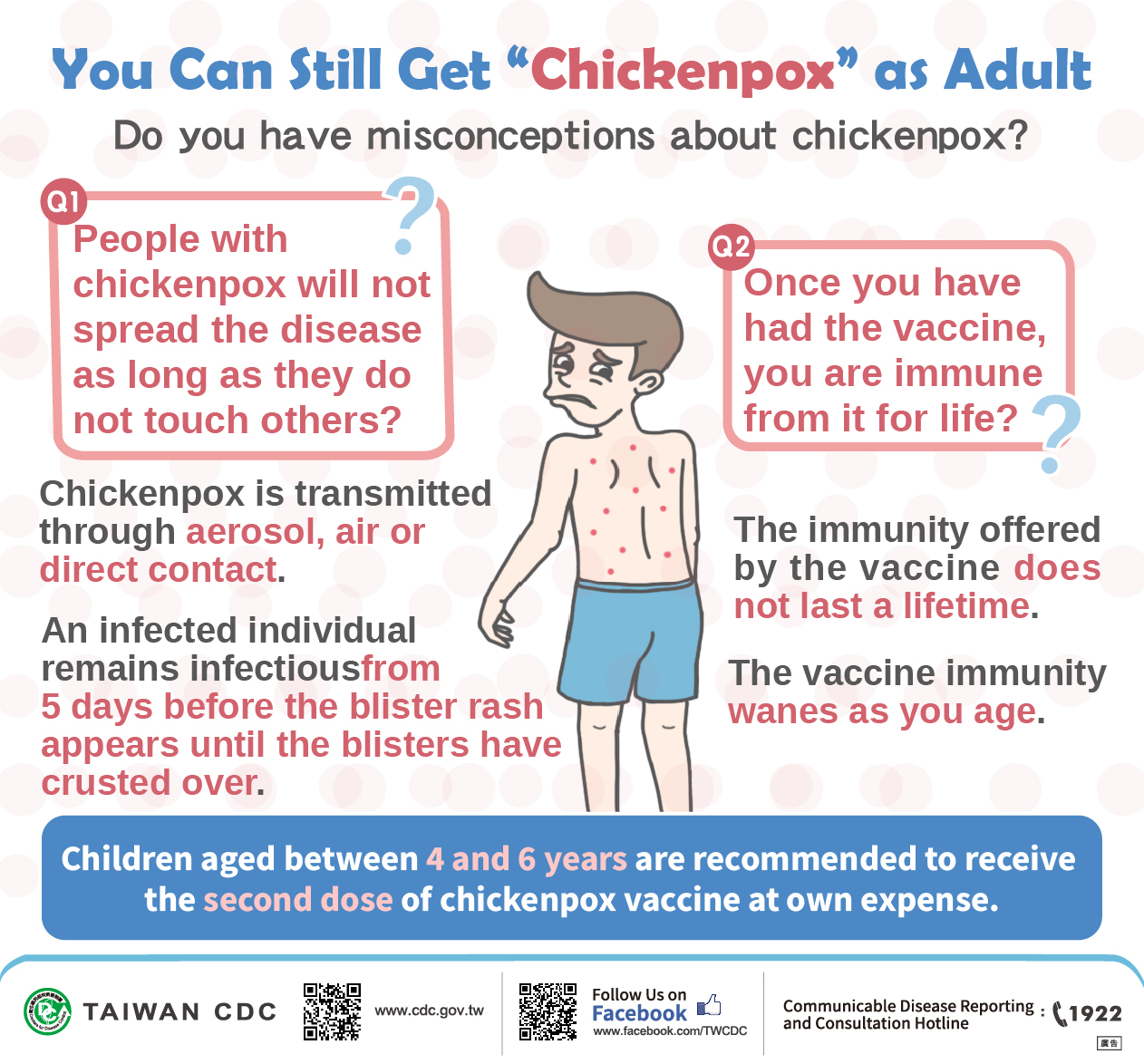
Varicella is a high infectious diseases caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), initial (1 to 2 days before rash) contains mild fever (37.5-39° C), fatigue, loss of appetite, headache and muscle or joint pain, after the skin began to rash, and gradually developed into red pimples, rash, pus rash and then scab, by the face, scalp to the trunk limbs, body rash gradually appear quickly blister, and finally left the granular crust (usually about two to four weeks to heal).
Complicated Varicella
Complications from varicella can occur, but they are not common in healthy people who get the disease. People who may get a serious case of varicella and may be at high risk for complications include infants, adults, pregnant women, people with weakened immune systems because of illness or medications.
Serious complications from varicella include bacterial infections of the skin and soft tissues, pneumonia, infection or inflammation of the brain (encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia), blood stream infections (sepsis), dehydration.
Some people with serious complications from varicella can become so sick that they need to be hospitalized. Varicella can also cause death.
Complicated Varicella Surveillance in Taiwan
Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
Prevention and Control
- The best way to prevent varicella is to get the varicella vaccine.
- Maintain good personal and environmental hygiene.
- Keep the indoor air circulation, to avoid long-term in a confined space.
- Keep your hands clean and wash your hands in the right way.
- Patients should follow respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette.
- Varicella patients should adhere to the principle of not going to work and not going to class.
FAQs
- What is varicella?
- Varicella is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It causes a blister-like rash, itching, tiredness, and fever. The rash can spread over the entire body.
- Varicella can be serious, especially in babies, adults, and people with weakened immune systems. The best way to prevent varicella is to get the Varicella vaccine
- What are the typical symptoms of varicella?
- The typical symptoms are:
- (1)fever
- (2)blister-like rash with severe itching all over the body
- (3)loss of appetite
- (4)tiredness
- If you have been vaccinated for varicella, some people can still get the disease, but it is usually mild with fewer blisters and low or no fever.
- The typical symptoms are:
- When is a person contagious?
- A person with varicella can spread the disease from 1 to 2 days before they get the rash until all their varicella blisters have formed scabs (usually 5-7 days).
- It takes about 2 weeks (from 10 to 21 days) after exposure to a person with varicella or shingles for someone to develop varicella.
More Information
USA CDC-Chickenpox (Varicella)
Images
Attached Files
About CDC
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
- National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
- Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal

