- About CDC
- Diseases & Conditions
- Programs & Campaigns
-
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
- National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
- Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal
- International Cooperation
-
About CDC
- Diseases & Conditions
-
Programs & Campaigns
-
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
-
National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
-
Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Weekly Report 2025
- Weekly Report 2024
- Weekly Report 2023
- Weekly Report 2022
- Weekly Report 2021
- Weekly Report 2020
- Weekly Report 2019
- Weekly Report 2018
- Weekly Report 2017
- Weekly Report 2016
- Weekly Report 2015
- Weekly Report 2014
- Weekly Report 2013
- Weekly Report 2012
- Weekly Report 2011
- Weekly Report 2010
- Weekly Report 2009
- Weekly Report 2008
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal
- International Cooperation
- News
- Privacy Policy
- Security Policy
- Government Website Open Information Announcement
- Copyright Notice on Health Educational Materials
Background
Syphilis is a persistent, highly infectious sexually transmitted disease (STD) that can cause serious health problems without treatment. It is caused by the spiral-shaped bacterium (spirochete) Treponema pallidum, which can live almost anywhere in human body and spreads rapidly. Syphilis develops in stages (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). Each stage has different signs and symptoms, and can last for several years. Without treatment, serious health complications are common and can be fatal in late-stage, or tertiary syphilis.
Epidemiology
In 2021, a total of 9,413 syphilis confirmed cases were reported in Taiwan. Among them, a total of 1,776 cases were defined as active syphilis (primary, secondary, tertiary), which the ratio of males to females was 11:1. Among active syphilis cases in 2021, the majority was cases with age group of 25 to 34 years-old (42%). The following was the age group of 35 to 44 years-old (21%). (See Figure 1)
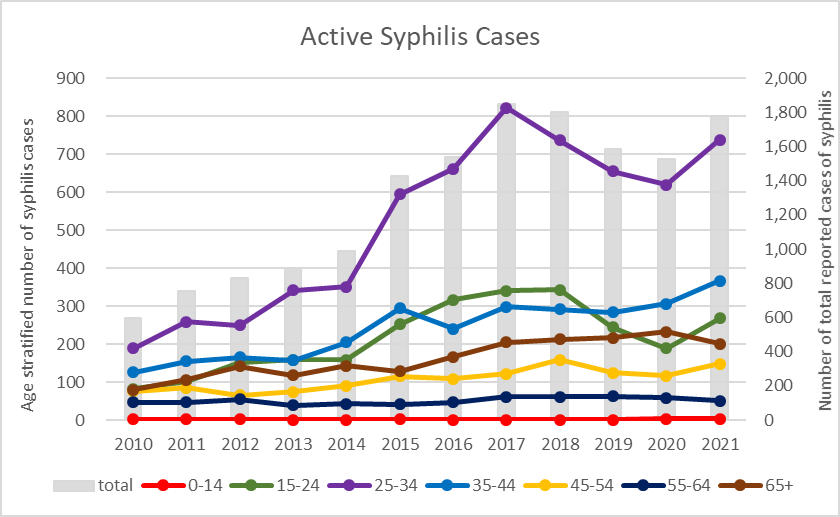
Figure 1. Statistics on age groups of active syphilis cases in Taiwan, 2010-2021
Prevention and Control
- To reduce syphilis transmission.
- To promote safe sex education for general population and STI screening for target population.
- To provide comprehensive case management, including correct diagnosis; effective treatment to avoid complications; health education and counseling.
FAQs
1. How is syphilis transmitted?
Syphilis is spread through vaginal, oral, and anal sex during the infection in primary, secondary, and early latent stages. The bacterium is usually transmitted by direct contact between mucous membranes of the genitals, mouth, or anus; or by broken skin coming into contact with open syphilitic sores. An infected mother can pass syphilis through the placenta to her developing fetus. Reinfection after cure is possible.
2.What is the treatment for syphilis?
A single intramuscular injection of penicillin is the standard treatment for primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis. For those allergic to penicillin, antibiotics such as tetracycline, doxycycline, minocycline, and ceftriaxone may be considered. Follow-up of treatment response by VDRL/RPR is necessary for about 1 year.
Penicillin can also be used to treat tertiary, or late stage syphilis, but cannot reverse damage that has occurred. However, syphilis in the central nervous system may not respond to penicillin during the tertiary stage, even when high doses are administered intravenously.
More Information
Images


About CDC
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
- National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
- Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal

