-
About CDC
- Diseases & Conditions
-
Programs & Campaigns
-
Data & Statistics
- Taiwan National Infectious Disease Statistics System
- Statistics of HIV/AIDS
- Disease Surveillance Express
- Influenza Express
-
National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Report
-
Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
Weekly Report of Enterovirus Infection
- Weekly Report 2025
- Weekly Report 2024
- Weekly Report 2023
- Weekly Report 2022
- Weekly Report 2021
- Weekly Report 2020
- Weekly Report 2019
- Weekly Report 2018
- Weekly Report 2017
- Weekly Report 2016
- Weekly Report 2015
- Weekly Report 2014
- Weekly Report 2013
- Weekly Report 2012
- Weekly Report 2011
- Weekly Report 2010
- Weekly Report 2009
- Weekly Report 2008
- Taiwan Healthcare-associated infection and Antimicrobial resistance Surveillance System
- Taiwan CDC Open Data Portal
- International Cooperation
- News
- Privacy Policy
- Security Policy
- Government Website Open Information Announcement
- Copyright Notice on Health Educational Materials
Background
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by Neisseria gonorrhea bacteria. Urethral infections in men and uro-genital infections in women are the main presenting feature, but a broad spectrum of clinical presentations can occur, including systemic dissemination with fever and skin and joint involvement. Throat and ano-rectal infections also occur.
(Case Definition)
Epidemiology
In 2021, a total of 7,381 cases of gonorrhea were reported in Taiwan. The ratio of males to females was 9:1. The majority was cases with age group of 25 to 34 years-old (39%). The following was the age group of 15 to 24 years-old (34%). (See Figure 1)
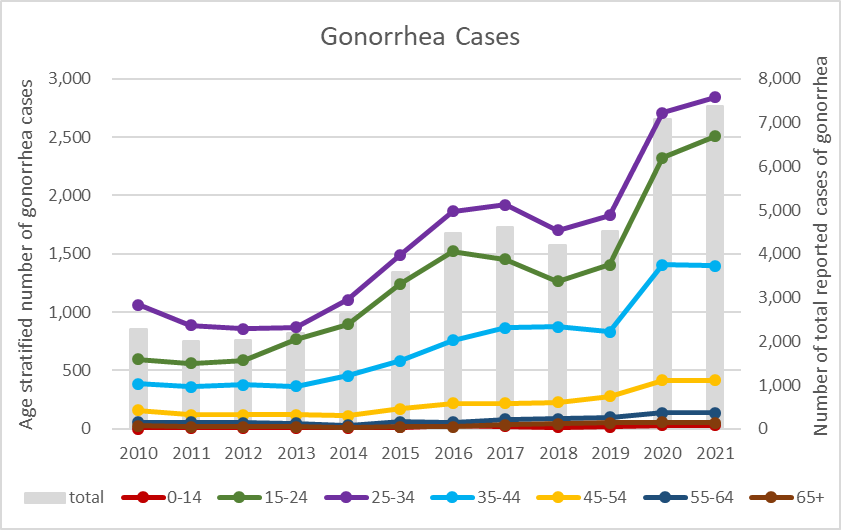
Figure 1. Statistics on age groups of gonorrhea cases in Taiwan, 2010-2021
Prevention and Control
- To reduce gonorrhea transmission.
- To promote safe sex education for general population and STI screening for target population.
- To provide comprehensive case management, including correct diagnosis; effective treatment to avoid complications; health education and counseling.
FAQs
- How is gonorrhea spread?
- You can get gonorrhea by having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has gonorrhea.
- If a pregnant woman has gonorrhea, she may give the infection to her baby during delivery as the baby passes through the birth canal. If untreated, infants can develop eye infections.
- What is the treatment for gonorrhea?
- Recommended treatment for uncomplicated infections is a third-generation cephalosporin or a fluoroquinolone plus an antibiotic (e.g., doxycycline) effective against possible coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis. Sex partner(s) should be referred and treated. No effective vaccine yet exists.
- Can gonorrhea be cured?
- Yes, gonorrhea can be cured with the right treatment. However, it is becoming harder to treat some gonorrhea, as drug-resistant strains of gonorrhea are increasing. If your symptoms continue for more than a few days after receiving treatment, you should return to a health care provider to be checked again.
More Information
圖片

為提供使用者有文書軟體選擇的權利,本網站提供ODF開放文件格式,建議您安裝免費開源軟體 (https://www.ndc.gov.tw/cp.aspx?n=32A75A78342B669D) 或以您慣用的軟體開啟文件。

